- Sample Questions for
2/3 Exam from Previous Years
- Click
on the "answer" term below for the answer and
explanation.
-
- Which test statistic --- (1)
z-score, (2) t-score, (3) F ratio ---- would be most
suitable for testing relationships between
- these pairs of
variables?
-
- 1.______ Difference
in mens' and womens' attendance rates at religious
services
-
- 2.______ Difference in the
predicted mean Republican vote in 1998 by the Gallup poll
with 900 interviews and the CBS poll with
1,200.
-
- 3.______ Literacy rates by
countries and a classification of countries by region.
Answers
for all three -
- 4. The formula
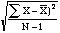 provides
an unbiased estimate of the population: provides
an unbiased estimate of the population:
|
1- standard
deviation
|
2- standard error
|
3- sum of
squares
|
4-
variance
|
Answer
- 5. The
standard error of the mean is
- 1- an unbiased estimate of the
population mean
- 2- equal to the standard
deviation of the sample data
- 3- the standard deviation of
the sampling distribution of means
- 4- the descriptive statistic
that measures dispersion
Answer
- 6. The
standard error of the mean is equal to
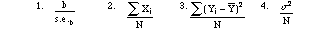 Answer
- 7. Given a
sample size of 100, mean of 36, population standard
deviation of 5, and confidence level of .95, the
confidence interval for the mean of the population is
closest to
|
1- 31 to 41
|
2- 26 to 46
|
3- 35.5 to
36.5
|
4- 35 to
37
|
Answer
- 8. In
practical terms, the amount of accuracy in predicting
from national samples to the U.S. Population is
least dependent on
- 1- the proportion that the
sample is of the population
- 2- the absolute number of cases
in the sample
- 3- the population variance for
the attribute being estimated
- 4- the procedure used in
drawing the sample
Answer
- 9. Which of
the following terms does not belong with the other
terms?
|
1- Type I
error
|
2- alpha
level
|
3- region of
rejection
|
4-
z-score
|
Answer
- 10. Which of
the following statistical distributions is interpreted
with reference to two different degrees of
freedom?
|
1- F
|
2- t
|
3-
skewed
|
4- normal
|
Answer
- 11. If one
has a directional hypothesis, he or she especially wants
to
- 1- make a one-tailed
test
- 2- make a two-tailed test
- 3- guard against a Type I error
- 4- guard against a Type II
error
Answer
- 12. The
sampling distribution of the difference between two means
for independent samples --
- 1- is unknown and therefore one
cannot test differences between two means against a
null hypothesis.
- 2- is not subject to the
Central Limit Theorem.
- 3- has a standard error equal
to the difference in the standard errors of the
individual samples.
- 4- tends to become normal as
the sample sizes increase.
Answer
- 13. In the
analysis of variance model, the null hypothesis of no
difference among the means for the subgroups will tend to
be rejected as
- 1- the "between group" variance
exceeds the "within group" variance.
- 2- the "within group" variance
begins to exceed the "between group"
variance.
- 3- the "within" and "between"
group variance approach equality.
- 4- both the "between" and the
"within" group variance approach total
variance.
Answer -
- 14. Which
statement is true about data expressed in
proportions?
- 1- You cannot treat proportions
as interval data.
- 2- You cannot compute variance
for a dichotomized variable expressed as
proportions.
- 3- Proportions computed for a
dichotomized variable are simply a type of
mean.
- 4- Transforming percentage data
into proportions is an example of a nonlinear
transformation.
Answer
- 15. Another
name for "between groups" sum of squares in the analysis
of variance is
- 1- unexplained variation
- 2- deviations about the
regression line
- 3- explained variation
- 4- error variance
Answer
- 16. An
unbiased estimator of a population parameter is
- 1- a statistic whose mean value
of its own sampling distribution is equal to the
population parameter.
- 2- a statistic with a
relatively small sampling error.
- 3- a statistic that predicts to
the population with a known bias.
- 4- impossible to calculate if
the population lacks a normal
distribution.
Answer
- 17. Calculate
the variance for this set of numbers: -5,-5,-5,5,5,5
- Variance =
_____
Answer
- 18. According
to the table of areas under the normal curve, what
positive and negative z-score value would be used to
establish the region of rejection for a TWO-tailed test
nearest to the .04 level of significance?
- z-score =
__________
Answer
-
- Here is T-TEST output comparing
Democrat and Republican Members of Congress, with the
dependent variable being a scale of
increasing"conservatism" in voting on social issues.
Answer questions 19 and 20.
VARIABLE NUMBER STANDARD STANDARD
OF CASES MEAN DEVIATION ERROR
DEMOCRATS 248 30.5806 23.441 1.488
REPUBLICANS 180 65.7278 16.318 1.216
Mean Difference = -35.1472
Levene's Test for Equality of Variances:F= 2.06 P= .000
Variances t-value df 2-TailSig
Equal -17.30 426 .000
Unequal -18.28 425.31 .000
|
|
- 19.Which
expression below was used to compute the degrees of
freedom for Equal Variance estimate of the T-Test above?
|
1- (N -
1)
|
2- (k -
1)
|
3- (N - 2)
|
4- (N1 + N2 - 2)
|
Answer
-
- 20. Which
statement about the above T-TEST output is true?
- 1- It shows that DEMOCRATS were
actually more conservative on social issues than
Republicans
- 2- It shows that REPUBLICANS
showed much more variation in voting on conservative
issues than DEMOCRATS.
- 3- The F-value is significant
at the .05 level, indicating that the population
variance are equal and that you are advised to use the
Unequal variance estimate rather than the Equal
estimate in checking the significance of
t.
- 4- Regardless of which estimate
you use, the T-TEST shows that both groups of
Representatives do NOT differ significantly in voting
on social issues, so the null hypothesis CANNOT be
rejected.
Answer
-
- Below is SPSSx output from MEANS
for GNP PER CAPITA in the POLITY data analyzed by type of
government. Answer questions 21, 22, 23, and 24 with
reference to this output.
-
DEPENDENT VARIABLE GNPPCA80 GNP PER CAPITA IN US DOLLARS-1980
INDEPENDENT VARIABLE POLTYPE TYPE OF POLITICAL SYSTEM
VARIABLE VALUE LABEL MEAN STD DEV CASES
FOR ENTIRE POPULATION 3633.0864 4267.0914 81
POLTYPE 1.00 PARLIAMENT/DEMOCRACY 6511.4815 4608.2098 27
POLTYPE 2.00 DEMOCRATIC & FEDERAL 9598.0000 5869.8825 5
POLTYPE 3.00 MULTIPARTY DEMOCRACY 1322.8571 1334.9746 7
POLTYPE 4.00 DEMOCRATIC FORM 2210.0000 113.1371 2
POLTYPE 5.00 MILITARY GOVERNMENT 895.8333 900.6408 12
POLTYPE 8.00 ONEPARTY COMMUNIST 3587.5000 2431.3180 8
POLTYPE 9.00 ONEPARTY SOCIALIST 2270.0000 494.9747 2
POLTYPE 10.00 ONEPARTY MARXIST 276.6667 140.1190 3
POLTYPE 11.00 ONEPARTY STATE 798.6667 1015.8168 15
SUM OF MEAN
SOURCE SQUARES D.F. SQUARE F SIG.
BETWEEN GROUPS 690959683.13 8
WITHIN GROUPS 765685845.26 72
|
|
- 21. Showing
the math, compute the MEAN SQUARE for BETWEEN GROUPS to
one decimal: _____________
Answer -
- 22. Showing
the math, compute the F ratio to one decimal:
_____________
Answer -
-
- 23. Which
statement gives the most accurate assessment of
that relationship?
- 1- The null hypothesis can be
rejected at the .10 level.
- 2- The null hypothesis can be
rejected at the .05 level.
- 3- The null hypothesis can be
rejected at the .01 level.
- 4- The observed differences in
GNP by government type can occur about 20 times out of
100 on the basis of chance alone.
Answer - 24. Under the
null hypothesis, the expected value of Pearson's r
is
- 1- dependent on sample size
- 2- not used in two-tailed tests
- 3- unknown unless the t value
is computed
- 4- zero
Answer
-
- 25. What
condition exists when the variance of Y remains the same
for different values of X?
|
1-
homoscedasticity
|
2-
unbiasedness
|
3-
normality
|
4-
linearity
|
Answer
-
- 26. This
formula for testing the significance of r:
 , assumes that
, assumes that
- 1- the F table is used to
determine level of significance.
- 2- that you have no degrees of
freedom in computing the significance.
- 3- there is no difference
between the observed and expected correlation.
- 4- the test is against the
null hypothesis that the population correlation, r
(rho), is equal to 0.
Answer
- 27. If
data for 2 variables are transformed into z-scores and
then correlated, [This
topic was not covered.]
- 1- the product
moment correlation will be equal to the beta coefficient
in the associated regression equation.
- 2- the beta
coefficient will be equal to the b-coefficient in the
regression equation.
- 3- the intercept
in the regression equation will be equal to
0.
- 4- all of the
above are true.
Answer -
- 28.Tested against
the null hypothesis, a highly significant correlation
merely indicates that
- 1- it is unlikely that there is
no relationship between the variables in the
universe.
- 2- knowledge of one variable
will substantially improve prediction of the value of
an observation on the other variable.
- 3- there is a strong
relationship between the variables in the
universe.
- 4- there is a strong
relationship between the variables in the
sample.
Answer - 29. Which
statistic is most appropriate for testing the
significance of the difference among means for four
independent samples?
|
1- t-test
|
2- beta coefficient
|
3- F ratio
|
4- b
coefficient
|
Answer
-
- 30. The
condition of heteroscedasticity is best shown in which
diagram?
 Answer -
-
|